Interposition: Learn This Monocular Depth Cue | Explained
Ever wondered how we instantly perceive depth in a two-dimensional image, like a photograph or a painting? The answer lies, in part, with a remarkable visual trick called interposition, a powerful depth cue that our brains use to interpret the world around us.
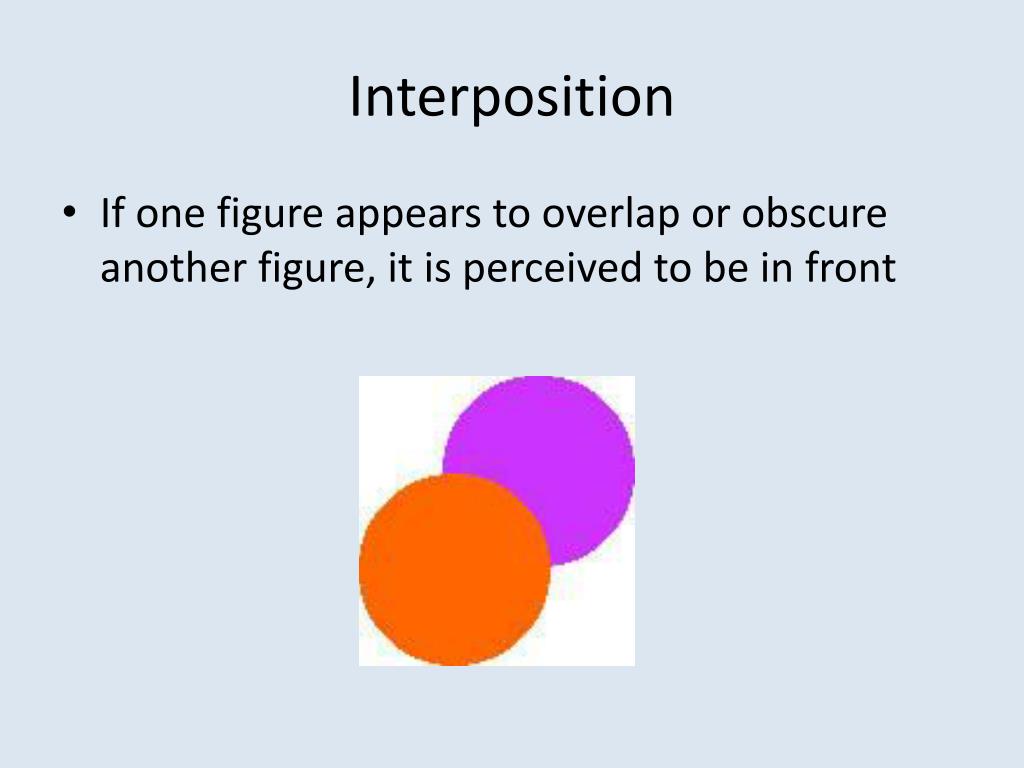
Interposition, a cornerstone of visual perception, allows us to decipher the spatial relationships between objects. This monocular depth cue, meaning it works with just one eye, provides critical information about which objects are closer and which are farther away. It's a simple concept: when one object partially blocks another, we perceive the obscured object as being further away. Think of it like this: a card placed in front of another gives the appearance of the other card being behind it, with the overlap creating the impression of one card being on top. This seemingly simple phenomenon has profound implications, extending beyond basic visual perception to influence how we understand space, art, and even social interactions.
Let's delve deeper into the mechanics of this visual phenomenon. Interposition, also known as occlusion, is one of several monocular cues that our visual system employs to create a three-dimensional representation of the world. These cues, which include texture gradient, linear perspective, aerial perspective, and relative size, work in concert to provide us with a rich and nuanced understanding of depth. While the term "interposition" may be unfamiliar to some, the underlying principle is something we encounter constantly. When looking at objects at different distances, the closer objects often partially obscure our view of those further away, instantly giving us a sense of their relative positions.
Consider a scenario: two trees stand in a field. One appears to partially cover the other. Our brains, using interposition, instantly interpret the partially obscured tree as being further away. This is an example of how our brains actively process visual information to create a coherent understanding of space. The effectiveness of interposition isn't always absolute; its impact on depth perception can be influenced by other cues. For instance, if the relative sizes, texture gradients, shading, or even perspective shift, the perception of depth can be altered or clarified. The same is true when multiple cues work in collaboration. In that case, interposition can reinforce or even override other depth cues, depending on the context.
Now, let's look at the broader significance of interposition. This visual phenomenon extends far beyond basic visual perception. Researchers have discovered that it also plays a key role in understanding object categorization and even object recognition. For example, studies have shown that interposition affects how we categorize objects within a scene and impacts our ability to correctly identify and understand objects in pictures or in a real-world situation. This is why interposition is a key concept in understanding how humans perceive depth and spatial relationships in their visual field. In the field of art and design, artists have long leveraged interposition as a powerful tool to create a sense of depth and realism. From the Renaissance masters to contemporary artists, the principle of interposition has played an essential part in visual storytelling. This principle also is applicable to everyday life; the use of interposition to determine the relative distances of objects is something we do constantly.
This technique has been around for centuries and continues to be used. For example, you may have seen a picture of a mountain landscape in a painting. In the painting, the mountains in the distance are more hazy than the ones in the foreground. This technique is known as aerial perspective, and it is also a depth cue. The mountains in the distance appear hazier because of the atmosphere and the distance. Interposition is also important in other areas of psychology. For example, it is used in social perception, where it plays a role in how we perceive the relationships between people and objects in our environment. It can also affect how we interpret facial expressions and body language.
The implications of interposition in the realm of art and design are profound. Painters, sculptors, and designers have harnessed this principle for centuries to create a sense of depth and realism in their work. By strategically overlapping objects, they can guide the viewer's eye and manipulate the perceived spatial relationships within a composition. Interposition, therefore, is more than just a visual cue; it's a fundamental tool for conveying depth, creating visual interest, and telling stories. It's important to understand the power of depth perception because it allows you to make judgments about the distance of objects in the world.
Interposition is a fundamental concept in understanding how humans perceive depth and spatial relationships in their visual field. It has its applications in several subfields of psychology. One of the most interesting applications of interposition psychology is the study of emotional behavior and human cognition, the interrelation of thought, emotion and behavior. It examines how thoughts influence and shape emotions, and how emotions, in turn, influence our cognitive processes. It also investigates the role of the self and its interactions with the environment in shaping psychological experiences.
In conclusion, interposition, a deceptively simple visual phenomenon, is a testament to the sophisticated processing capabilities of the human brain. By understanding how we perceive depth and distance, we gain a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of our visual world. From the art of the masters to the everyday act of navigating our surroundings, interposition plays an indispensable role in how we make sense of the spaces around us.
Disclaimer:The following information is presented for informational purposes only and should not be considered as professional advice. Always consult with a qualified expert for any specific concerns.