Letrozole & Spotting: What You Need To Know Now
Is a persistent change in your menstrual cycle a cause for immediate concern, or is it simply a side effect of medication? Navigating the complexities of hormonal therapies like letrozole often involves understanding how they impact your body, and recognizing when to seek medical advice is crucial.
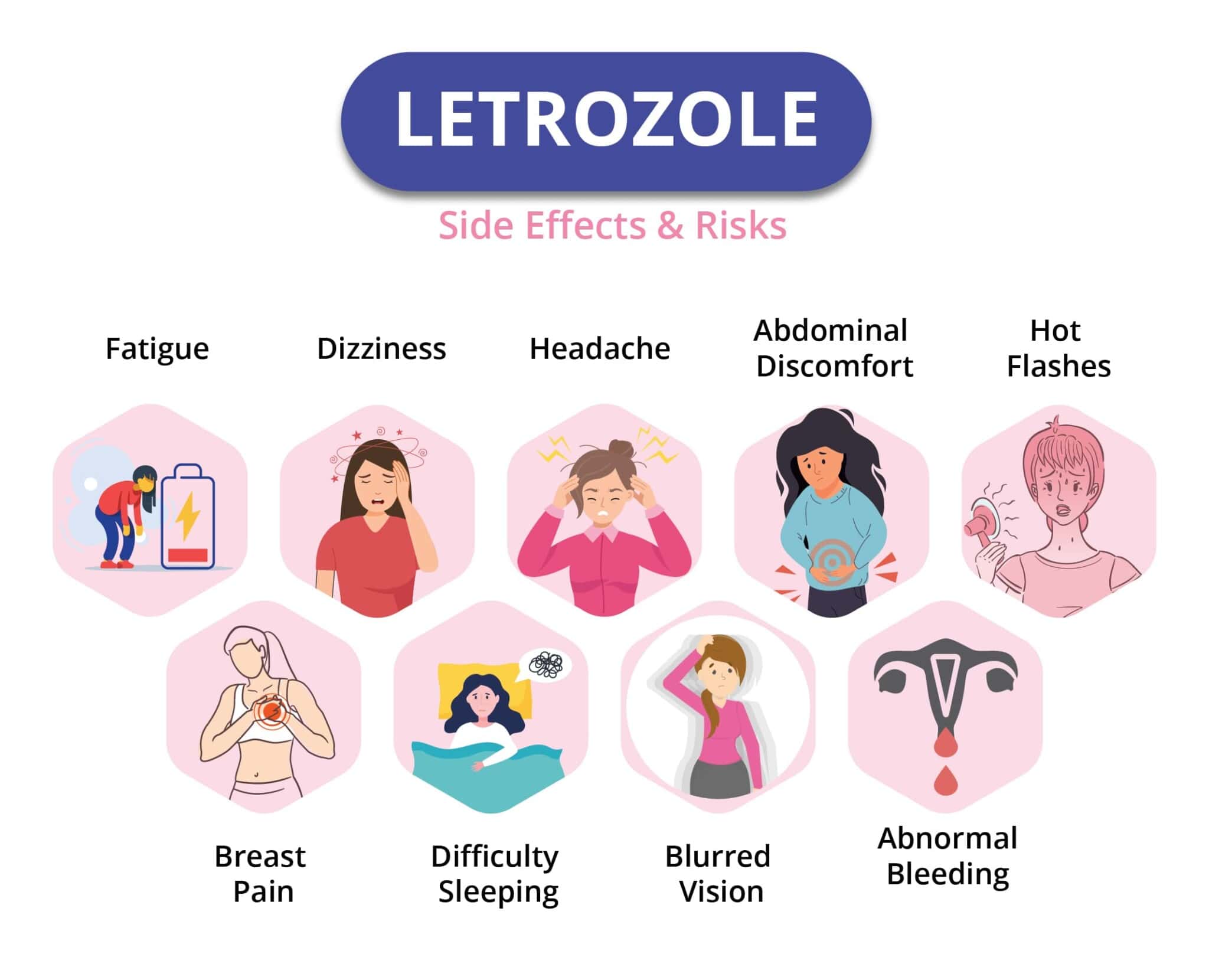
Many women undergoing treatment with letrozole, a drug frequently used to treat certain types of breast cancer, experience alterations in their menstrual cycle. These changes can manifest in several ways, from extended periods and heavier bleeding to breakthrough spotting, even when not expecting their period. It's essential to understand that these symptoms are often related to the medications mechanism of action and its effects on hormone levels. The drug, a generic prescription known by the brand name Femara, works by reducing estrogen production in the body. This reduction in estrogen can influence the uterine lining, the endometrium, and consequently, the menstrual cycle.
Letrozole's role in breast cancer treatment stems from its ability to inhibit aromatase, an enzyme that converts other hormones into estrogen. By decreasing estrogen, letrozole can slow or halt the growth of hormone-sensitive breast cancers. However, this hormonal shift can lead to various side effects, including changes in vaginal bleeding patterns. Patients might encounter spotting, which is light vaginal bleeding occurring outside of their regular periods. This can be particularly concerning if the bleeding is unusual in nature or duration, and the specific experience can vary among individuals.
Clinical studies have documented that spotting is a relatively common occurrence for those taking letrozole. The intensity and duration of spotting can vary, with some women experiencing only a few days of light bleeding, while others may have more prolonged or heavier spotting. The underlying causes of this spotting can range from the medications direct impact on the endometrium to the potential for vaginal dryness, another side effect linked to reduced estrogen levels. In some cases, the changes in bleeding patterns might be a direct result of switching between different hormone therapies, something often encountered in cancer treatment protocols.
The following table presents a detailed overview of Letrozole, its uses, and associated side effects, offering a comprehensive understanding of the medication:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Generic Name | Letrozole |
| Brand Name | Femara |
| Primary Use | Treatment of certain types of breast cancer, particularly hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. |
| Mechanism of Action | Inhibits aromatase, an enzyme that converts other hormones into estrogen, thereby reducing estrogen levels. |
| Common Side Effects | Hot flashes, joint pain, fatigue, night sweats, bone loss, vaginal dryness, and changes in vaginal bleeding patterns (spotting). |
| Serious Side Effects | Fast heart rate (palpitations), chest pain, and allergic reactions. |
| Menstrual Cycle Impact | May cause irregular bleeding, spotting, longer periods, or the absence of periods. This is due to the reduction in estrogen, which affects the uterine lining. |
| Monitoring and Management | Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential. Report any significant or unusual bleeding patterns. Symptoms like severe side effects should be reported immediately. |
| Considerations | May require lifestyle adjustments (exercise, diet) to manage certain side effects. Discuss any symptoms with your doctor and consider alternative treatments or management strategies as necessary. |
| Important Note | If bleeding continues for more than a few days or if you experience heavy bleeding, it is crucial to consult with your specialist or healthcare provider immediately. |
| Reference | Mayo Clinic: Letrozole |
Beyond the general information about spotting, it is also important to consider the various factors that influence menstrual patterns, which can be affected by any change in a womans overall health. As estrogen levels drop due to letrozole use, the uterine lining can become thinner, potentially leading to spotting. The endometrial lining's behavior plays a critical role in menstrual cycles: estrogen usually causes the lining to thicken in preparation for possible pregnancy and the absence of this can impact the shedding process.
The experience of women taking letrozole highlights a need for careful monitoring. One individual described experiencing light brown/light pink blood on day 10 of her cycle after starting the medication, which is common. Another shared that their periods were usually longer with much more after period spotting while on letrozole, adding to the information that it is not unusual for the drug to disrupt the normal menstrual cycle. These firsthand accounts show the range of possible experiences that women have while taking this drug.
The impact of letrozole on the menstrual cycle may also be compounded by its interaction with other medications or therapies. One user reported using letrozole alongside zoladex, another medication, that can further affect the hormonal environment. When multiple medications are involved, it is increasingly important to monitor any changes to the menstrual cycle.
Spotting can be a source of concern, and it's understandable to be worried about it. It's important to distinguish spotting from other conditions, like the type of bleeding related to early pregnancy. Early pregnancy bleeding, often called implantation bleeding, is caused by the fertilized egg embedding into the uterine lining. While letrozole patients may still become pregnant, spotting caused by the drug itself is not a dependable sign of pregnancy.
It is crucial to remain vigilant regarding the potential for serious side effects. Allergic reactions to letrozole are rare, but they require immediate attention. Symptoms of an allergic reaction include skin rash, itching, swelling of the face, tongue, throat, or neck, severe dizziness, and trouble breathing. Experiencing fast heart rate or chest pain while on letrozole requires immediate medical evaluation.
Recent studies have aimed to fully understand the side effects related to aromatase inhibitors like letrozole. Although many patients encounter some type of spotting or irregular bleeding during treatment, the majority of these cases do not indicate the onset of severe complications. However, this does not diminish the need to seek advice when unusual bleeding patterns emerge.
If you're experiencing unexpected or prolonged bleeding while taking letrozole, it's essential to communicate with your healthcare provider. They can assess your specific situation, considering your medical history, the dosage of letrozole, and other medications you may be taking. They might perform additional tests to rule out other possible causes of the bleeding or change the treatment plan.
Theres an ongoing effort in the medical community to better understand and address the side effects related to letrozole. Research continues to refine treatment strategies and help patients manage these side effects more effectively. The goal is to minimize any disruptions to womens lives while receiving potentially life-saving treatments.
As a patient, you are encouraged to become well-informed about your treatment and to ask questions to ensure the best health outcomes. Being informed involves knowing what to expect regarding potential side effects and knowing how to handle any changes in your body during treatment.
In conclusion, the experience of bleeding irregularities during letrozole treatment is common and frequently related to how the drug interacts with the bodys hormones. While the cause of spotting is usually not severe, women should remain alert and promptly report any substantial or unusual bleeding patterns to their healthcare providers for proper evaluation and care.